devel-tester-wiki
In Progress
Say hello to Wily Werewolf! 
Wiki Upgrade Note
This site is currently under construction. It will deal with Ubuntu development release and some how to's with crash recovery methods and techiques.

Disclaimer
The author of this wiki is not responsible for udpating the wiki data in some of the links that are provided here in devel-testers-wiki. The Mir, SystemD , Unity8 and Wayland wikis and the accuracy of the information therein is the responsiblity of the developers of those projects, however, time permitting, I may append and update outdated information in those areas.
Introduction
Say hello to Wily Werewolf, the next cycle of the most secure operating system on the planet, Ubuntu! Wily will deal with parsing down and cutting away floss and fancy yet still be punchy, snappy and attractive with increased effervescence and even more easy to work with on the desktop and mobile environment.More work on Mir, SystemD, Unity8 and convergence will continue in earnest. Ubuntu, with it's nearly impervious monolithic kernel, will do away with the need for clunky antimalware/virus programs and superfluous firewall systems that munch and hack away at vital resources on all the various different form factors that are available today. Ubuntu does away with nonsense and provides an environment where work can actually be done more efficiently than ever before. But working with Ubuntu is not all an arduous task that requires expert diligence to test and explore. Ubuntu injects a high level of fun and community where all can be involved and testing can actually be a very fulfilling experience. And now , with increased and intense development of Mir and Unity8 the Desktop Experience will be more exciting that ever before.
Notes and Links to be forthcoming when they are made available. UbuntuForums Release Schedule Sticky and Common Helper Make sure to edit Ubuntu.info file
New method to make bootable start-up disks.
Wily Werewolf Daily Image ISOs Xubuntu Wily Werewolf Daily Image ISOs Lubuntu Wily Werewolf Daily Image ISOs Kubuntu Wily Werewolf Daily Live Image ISOs Edubuntu Wily Werewolf Daily Live ISOs Wily Werewolf Daily Live Image ISOs Ubuntu Desktop-Next Wily Daily Image ISOs Ubuntu Mate Wily Daily Image ISOs Ubuntu-Gnome Wily Daily Image ISOs Ubuntu Core Wily Daily Image gz
Here are some common codes of interest to help with Utopic recovery in the event of a crash. How to find your sources.list - this list is used to set repositories and can be done manually. It is also informative to have on hand if you decide to do a transitional upgrade from Oneiric Ocelot to Precise Pangolin or upcoming Trusty Tahr, now Utopic Unicorn. Here is a list of commonly used Ubuntu/Linux terminal Codes (not necessarily in order and open to interpretation) of WW Crash Recovery Codes -To be updated:
There has been a lot of hot debate topic at Ubuntuforums about the Ubiquity Installer, UEFI and some suggestions at possible changes that can be made. The Ubiquity "greeter" is the first GUI program that is loaded after the Plymouth logo. It presents two options after you boot from your DVD or USB flash drive. First, to 'Try Ubuntu' in the 'live' session. That means that a live session of the version of Ubuntu you are running will load into memory and you can run basic programs and even your internet browser to give Ubuntu a trial run. Secondly, there is the "Install Ubuntu" option which will install Ubuntu to your hdd (hard drive).If you have another operating system on your hard drive, (hdd for short), the Ubuntu Installer will detect it and will then guide you through an easy installation process. You can also "Install Ubuntu" from the "live" session by double clicking the "Install Ubuntu" icon. Ubiquity is designed mostly to work in an automated fashion for STANDARD machines. A STANDARD machine is usually a laptop or desktop that was originally configured with a Windows Operating System in a factory. That Operating System could be ME, Win 2000, XP, Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8 etc.. A STANDARD machine is most often configured with ONE hard drive! If there is more than one hard drive or if there is another operating system installed alongside the Windows operating system it becomes a CUSTOM install. Ubiquity, during the installation process and configuration of the hard drive, will give you options to install ubuntu alongside, upgrade or erase and remove. It will also give you an option of <something else> which I will discuss soon. The SOMETHING ELSE option can be used for both STANDARD and CUSTOM systems but should be used exclusivley if you are building or working with a CUSTOM system that has more than one hard drive or a RAID array. All in all the installation process can be very easy , or, in many cases, very complex. The best possible way to help others understand is to present hot-links in this section. That would mean active links from Ubuntuforums Development Version and other partners and sources in the Ubuntu community infrastructure. This way all the bases can be covered and possibly make for a smoother transition from obsoleted Windows operating systems to upgraded Ubuntu versions that may be able to utilize your existing desktop or laptop in a more efficient manner. Links will be forthcomming. I apologize for taking such a long period of time to get this section updated. Regards .. Ventrical UbuntuForums Installer Tutorial UbuntuForums Ubiquity Discussion +UbuntuForums Ubiquity Discussion
Sudo command link to remove ppas
Ideas: We should use MoinMoin Syntax Parsers (http://moinmo.in/HelpOnParsers) where commands/code are presented. Parsers ensure code/commands are not converted to smileys and other MoinMoin stuff, therefore presented without errors. Log files: A lot of people don't know they exist, where they are stored, the type of information available in each log file, how to open them, how to search them easily for valuable information. New Beta Testers Warnings
Wily Werewolf is the codename for the new development cycle. If you are a new Beta tester and want to upgrade your repositories to the new development cycle then you must be advised that there are certain risks of breakage that could take place on your system(s). it is always advised that you have an extra system (hardware) or an extra harddrive to experiment with. If you are not familiar with experimenting with computer hardware or software then U+1 is not the forum for you, however, if you are willing to be on the cutting edge of Ubuntu release and understand that there could be breakage and want to contribute then the Ubuntu community welcomes you and your valued contributions. New Notes About the Release Schedule
Special note about Main Server
Make sure you choose Main Server from Other Software after you change your sources list.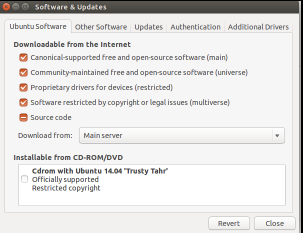
New stable method of flashing USBs with .ISOs
Startup Disk Creator has been having problems with reliability. Below is a link where Ubuntu developers/testers found a more stable method to make startup disks on USB flash drives. Download ISO
Some sudo Command Definitions
sudo basically means superusers-do. It is the basic command that gives access to administrative files that may need root authentication. There is a large database on sudo and sudoers definitions and uses in the following links. SudoUbuntuManuals and SudoersUbuntuManual 

















Instructional Development
Ubiquity Installer
Animated Terminal Instructions for Update/Upgrade


Alternative Boot Method with SystemD
How to purge and remove ppas
pkexec testing
Much debate has taken place over using sudo, gksu or pkexec. You will have to decide for yourself which is most secure. Mir Testing
If you are interested in installing Mir to test during this cycle then you can use the following links. Note that the Mir wiki has only had minimal updating and so it is not entirely current. It may be better to use the Manually use Sudo Commands link to install Mir and it's components. Here is an UbuntuForum thread where some of us have been doing some preliminary testing. Unity8 Testing
![]()
![]()
Todo
EDIT:I'll contribute to this portion - I already have something written, as well as log searching scripts posted at Ubuntu+1 threads (posted by Effenberg0x0) ![]()
![]()
![]()
devel-tester-wiki (last edited 2015-05-12 03:53:18 by dale-f-beaudoin)
