Patches
|
Size: 9141
Comment:
|
← Revision 40 as of 2017-10-10 04:48:25 ⇥
Size: 8594
Comment: update for UQT conversion to git
|
| Deletions are marked like this. | Additions are marked like this. |
| Line 92: | Line 92: |
=== Patch Systems === <<Include(PackagingGuide/Intro/PatchesPatchSystems, , from="StartEnglish", to="EndEnglish")>> === Forwarding Patches Upstream === <<Include(PackagingGuide/Intro/PatchesForwarding, , from="StartEnglish", to="EndEnglish")>> |
|
| Line 107: | Line 114: |
| Attachments that are patches can be flagged in the Launchpad bug tracker, which then makes them show up in search results and on other reports. Attachments to bug reports appear in the attachments portlet on the right hand side of a bug report. | Attachments that are patches can be flagged in the Launchpad bug tracker, which then makes them show up in search results and on other reports. Attachments to bug reports appear in the attachments portlet on the right hand side of a bug report. Attachments which are flagged as patches have a special icon of a pair of Band-Aids beside them. |
| Line 109: | Line 116: |
| {{attachment:attachment-portlet.png}} The third attachment has a star by it, which indicates that this attachment is flagged as a patch. However, these stars do not normally show up in Launchpad, they require the [[ http://bazaar.launchpad.net/~gm-dev-launchpad/launchpad-gm-scripts/master/files | lp_patches ]] Greasemonkey script. You can install the script by clicking the green download arrow on the right hand side if you have greasemonkey installed. |
{{attachment:patch_portlet.png}} |
| Line 126: | Line 131: |
| Additionally, one could incorporate the patch into a debdiff for the package in the development release of Ubuntu or apply the patch to a bzr branch of the package and link the branch to the bug report. | |
| Line 129: | Line 132: |
| == Bugs with patches == | == Bugs that already have patches == |
| Line 135: | Line 138: |
| In the event that it is not a debdiff one could incorporate the patch into a debdiff for the latest release of Ubuntu or apply the patch to a bzr branch of the package and link the branch to the bug report. | == Bugs with verified patches == |
| Line 137: | Line 140: |
| If an attachment is a debdiff and applies to a recent version of the package the bug report needs to be [[ SponsorshipProcess | sponsored ]] to the appropriate archive. This is done by subscribing (NOT assigning) the appropriate sponsorship team to the bug. For packages in main and restricted the ubuntu-main-sponsors team should be subscribed. For packages in the universe and multiverse repositories the ubuntu-universe-sponsors team should be subscribed. You can view their queues at [[ https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+bugs?field.subscriber=ubuntu-main-sponsors | main-sponsors ]] and [[ https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+bugs?field.subscriber=ubuntu-universe-sponsors | universe-sponsors ]]. | As mentioned above, patches can come in several different forms. If the patch is not a debdiff one could incorporate the patch into a debdiff for the latest release of Ubuntu or apply the patch to a bzr branch of the package and link the branch to the bug report. If a patch is a debdiff and applies to a recent version of the package the bug report needs to be [[ SponsorshipProcess | sponsored ]] to the archive. This is done by subscribing (NOT assigning) the sponsorship team (ubuntu-sponsors) to the bug. You can view the queue at [[ https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+bugs?field.subscriber=ubuntu-sponsors | ubuntu-sponsors ]]. <<Include(PackagingGuide/Intro/PatchInclusion, , from="StartEnglish", to="EndEnglish")>> |
| Line 142: | Line 149: |
| * How to work with [[PackagingGuide/Complete#Patch%20Systems|patch systems]] | |
| Line 149: | Line 157: |
| * [[ https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+bugs?field.subscriber=ubuntu-main-sponsors | Main queue ]] - Bug reports in the sponsorship queue for main. * [[ https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+bugs?field.subscriber=ubuntu-universe-sponsors | Universe queue ]] - Bug reports in the sponsorship queue for universe. |
* [[ https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+bugs?field.subscriber=ubuntu-sponsors | Sponsorship queue ]] - Bug reports in the sponsorship queue. |
| Line 154: | Line 161: |
| * [[ http://bazaar.launchpad.net/~ubuntu-bugcontrol/ubuntu-qa-tools/master/files | ubuntu-qa-tools ]] - This project contains a couple of scripts that use Launchpadlib to facilitate flagging, or unflagging, of attachments as patches and adding a comment. | * [[https://git.launchpad.net/ubuntu-qa-tools | ubuntu-qa-tools ]] - This project contains a couple of scripts that use Launchpadlib to facilitate flagging, or unflagging, of attachments as patches and adding a comment. |
|
Definition
What is a patch? A patch is a change to an Ubuntu package that will resolve a bug report. These include:
- changes to the packaging of an Ubuntu package
- changes to the source code included in an Ubuntu package
These changes can appear in a few different formats:
diff
A diff is a plain text file that contains differences between the original file and changed file.
Example:
diff -Nurp ciso-1.0.0/ciso.h ciso-1.0.0-fixed/ciso.h
--- ciso-1.0.0/ciso.h 2006-11-03 12:53:02.000000000 -0800
+++ ciso-1.0.0-fixed/ciso.h 2008-11-27 13:32:01.000000000 -0800
@@ -28,9 +28,9 @@
typedef struct ciso_header
{
unsigned char magic[4]; /* +00 : 'C','I','S','O' */
-unsigned long header_size; /* +04 : header size (==0x18) */
+uint32_t header_size; /* +04 : header size (==0x18) */
unsigned long long total_bytes; /* +08 : number of original data size */
-unsigned long block_size; /* +10 : number of compressed block size */
+uint32_t block_size; /* +10 : number of compressed block size */
unsigned char ver; /* +14 : version 01 */
unsigned char align; /* +15 : align of index value */
unsigned char rsv_06[2]; /* +16 : reserved */Here the file ciso.h is being changed in two places. Notice that a line marked in front with a - indicates the line which is being removed and a line marked with a + indicates the line that is being added.
debdiff
A debdiff contains all the changes needed to build a different version of a package. The debdiff will probably include changes to the source of the package, in the form of a diff, in addition to files in the debian directory.
Shortened Example:
diff -u ciso-1.0.0/debian/rules ciso-1.0.0/debian/rules
--- ciso-1.0.0/debian/rules
+++ ciso-1.0.0/debian/rules
@@ -20,8 +20,10 @@
CFLAGS += -O2
endif
+include /usr/share/dpatch/dpatch.make
+
configure: configure-stamp
-configure-stamp:
+configure-stamp: patch
dh_testdir
# Add here commands to configure the package.
@@ -39,7 +41,9 @@
touch $@
-clean:
+clean: clean-patched unpatch
+
+clean-patched:
dh_testdir
dh_testroot
rm -f build-stamp configure-stamp
@@ -86 +90 @@
-.PHONY: build clean binary-indep binary-arch binary install configure
+.PHONY: build clean clean-patched binary-indep binary-arch binary install configure
diff -u ciso-1.0.0/debian/control ciso-1.0.0/debian/control
--- ciso-1.0.0/debian/control
+++ ciso-1.0.0/debian/control
@@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
Source: ciso
Section: utils
Priority: optional
-Maintainer: Gaëtan Petit <tenshu@gmail.com>
-Build-Depends: debhelper (>= 5), zlib1g-dev
+Maintainer: Ubuntu MOTU Developers <ubuntu-motu@lists.ubuntu.com>
+XSBC-Original-Maintainer: Gaëtan Petit <tenshu@gmail.com>
+Build-Depends: debhelper (>= 5), zlib1g-dev, dpatch
Standards-Version: 3.7.2Here the files debian/rules and debian/control are being modified.
Patch Systems
Forwarding Patches Upstream
Other
A patch could also be an image file, in the event that a package is missing a menu icon. Bug 274714 is a great example of this. In the debdiff the image is uuencoded (converted from binary to text) and looks like:
--- system-cleaner-1.10.3.orig/debian/system-cleaner-gtk.png.uuencode
+++ system-cleaner-1.10.3/debian/system-cleaner-gtk.png.uuencode
@@ -0,0 +1,429 @@
+begin 644 system-cleaner-gtk.png
+MB5!.1PT*&@H````-24A$4@```!@````8"`8```#@=SWX````!'-"250("`@(
+M?`ADB`````EP2%ES```+$@``"Q(!TMU^_````"5T15AT4V]F='=A<F4`36%C
Patches in Launchpad
Attachments that are patches can be flagged in the Launchpad bug tracker, which then makes them show up in search results and on other reports. Attachments to bug reports appear in the attachments portlet on the right hand side of a bug report. Attachments which are flagged as patches have a special icon of a pair of Band-Aids beside them.

Notice the "edit" link next to each attachment, it will take you to the following page:
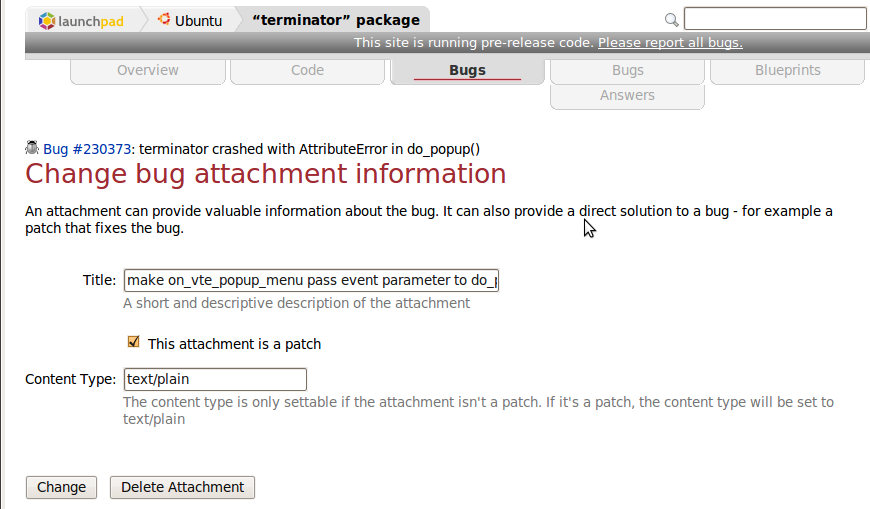
Here you can set and unset the patch flag on a per attachment basis.
Workflow
Bugs with attachments
Bug reports that have attachments should be examined to see whether or not any of those attachments are patches. If an attachment qualifies as a patch it should be flagged as one. When flagging attachments as patches comment on the bug indicating that the attachment was flagged as a patch and why this is important. A possible reply:
Looking at the attachments in this bug report, I noticed that an attachment was not flagged as a patch. A patch contains changes to an Ubuntu package that will resolve a bug and this attachment is one! Subsequently, I've checked the patch flag for it. In the future when submitting patches please use the patch checkbox as there are some Launchpad searches that use this feature. You can learn more about the patch workflow at https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Bugs/Patches. |
Bugs that already have patches
Bug reports that have attachments flagged as patches should have the patches reviewed to ensure that they are in fact patches. If an attachment is incorrectly flagged as a patch when it is not one, unflag the attachment and comment on the bug report indicating that the attachment is not a patch and why it is important for them to be identified properly. A possible reply:
Looking at the attachments in this bug report, I noticed that one was flagged as a patch incorrectly. A patch contains changes to an Ubuntu package that will resolve a bug, since this was not one I've unchecked the patch flag for it. In the future keep in mind the definition of a patch. You can learn more about what qualifies as a patch at https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Bugs/Patches. Thanks! |
Bugs with verified patches
As mentioned above, patches can come in several different forms. If the patch is not a debdiff one could incorporate the patch into a debdiff for the latest release of Ubuntu or apply the patch to a bzr branch of the package and link the branch to the bug report.
If a patch is a debdiff and applies to a recent version of the package the bug report needs to be sponsored to the archive. This is done by subscribing (NOT assigning) the sponsorship team (ubuntu-sponsors) to the bug. You can view the queue at ubuntu-sponsors.
Find out more:
How to fix bugs
What makes a good patch
How to work with patch systems
Resources
There are some customized Launchpad reports that can help with the patch workflow.
Bugs with attachments flagged as patches - These should be made into debdiffs or if they are not a patch the attachment should be unflagged.
Bugs with possible patches attached - In the event that the attachment to a bug report is discovered to be a patch it should be flagged as one.
Sponsorship queue - Bug reports in the sponsorship queue.
Tools
ubuntu-qa-tools - This project contains a couple of scripts that use Launchpadlib to facilitate flagging, or unflagging, of attachments as patches and adding a comment.
Bugs/Patches (last edited 2017-10-10 04:48:25 by sbeattie)
 This page is part of the
This page is part of the