ChromiumTouch
Chromium Integration
Contents
Introduction
This page describes the integration of frame and grail with Chromium to enable sophisticated gesture recognition within Chromium (and Chrome). Both the architectural and technical aspects of the patch (appended to this page) are explored. The summary concludes with a list of open issues/work items.
Chromium Architecture
Chromium is a cross-platform web browser built on top of WebKit and serves as a basis for Google Chrome. Moreover, it serves as the basis of ChromeOS. From an architectural point of view, the overall system can be divided up into two components:
- The UI component
The WebKit component
In the UI component, different platforms and/or GUI toolkits are abstracted in terms of so called modules. Within every module, platform specific bits and pieces are defined and implemented in files that are named in a platform specific manner (e.g., by appending _x11 to the filename).
Crossing the boundary between the UI component and the components glueing WebKit functionality to Chromium-specific bits and pieces is realized by an IPC mechanism.
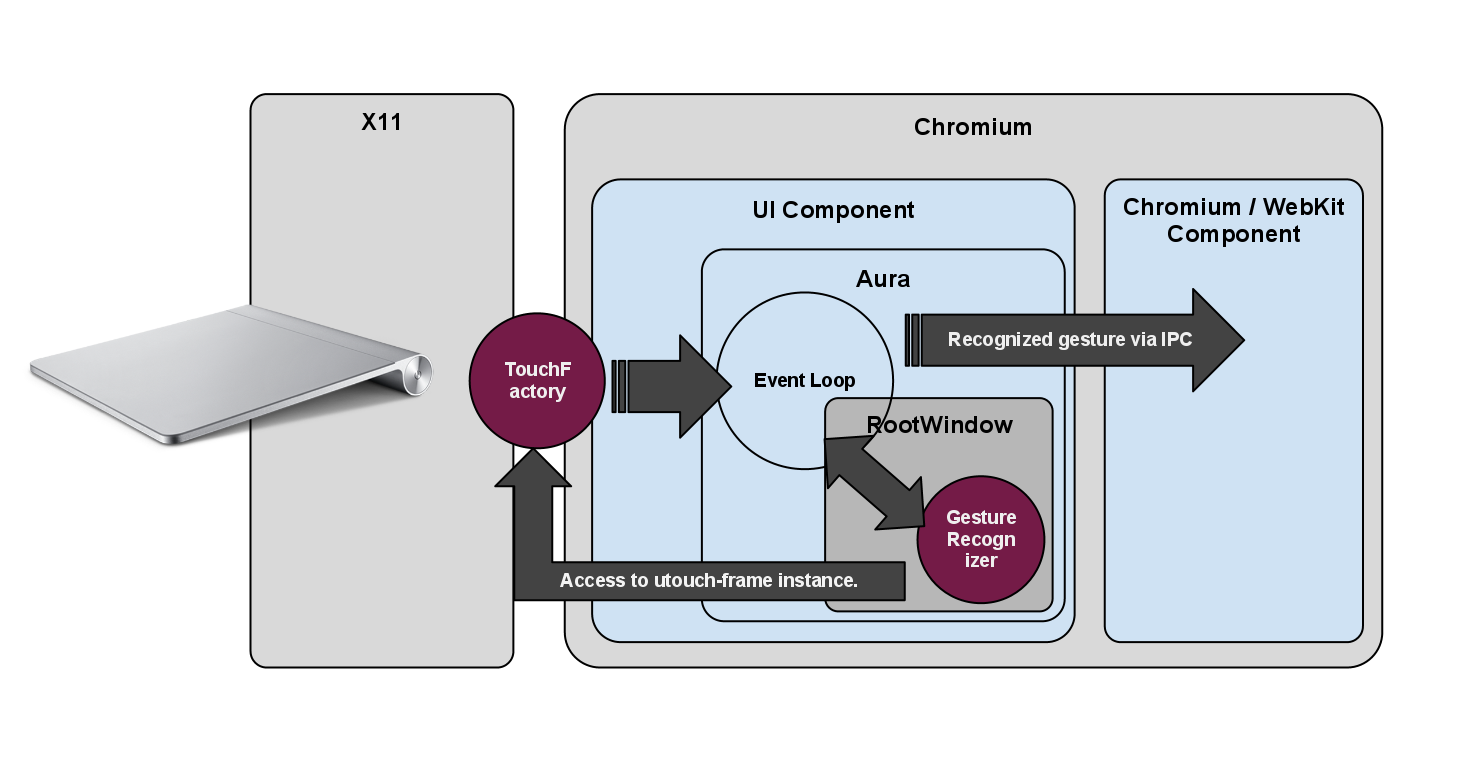
MultiTouch & Gesture Recognition Architecture
Both WebKit and WebKit Chromium define interfaces and types related to processing input from multi-touch devices and carrying out gesture recognition tasks. Only recently, these interfaces and types have been moved to the UI component of Chromium, more specifically to the Aura subcomponent. Aura is a GUI Toolkit abstraction that works on top of OpenGL ES 2.0 and will eventually become the basis for implementing both Chromium's and ChromeOS's user interface across all major platforms.
In Aura, handling of multi-touch devices is carried out by the singleton TouchFactory (ui/base/touch/touch_factory.h). Currently, its implementation (ui/base/touch/touch_factory.cc) relies on X11 and XI2.x. In general, the class takes care of:
- Maintaining a list of currently connected direct-touch devices
- Setting up event processing for these devices
The patch accompanying this document extends the functionality of the class by associating a frame instance with every instance of the class. Every XI2.x event is passed through frame (relying on its default X11/XI2.1 backend). Moreover, the frame instance is exposed to other classes for gesture recognition purposes. Finally, we altered the class TouchFactory to provide support for dependent touch devices like the Apple Magic Trackpad.
Gesture recognition tasks are abstracted by the interface GestureRecognizer (ui/aura/gestures/GestureRecognizer.h). Our modifications introduce an implementation of this interface in terms of grail and provide recognition of:
- Two-finger drag gestures
- Two-finger pinch gestures
- One- and two-finger tap gestures
both on direct and dependent touch devices (thanks to the modifications to TouchFactory). Every instance of an implementation of the interface GestureRecognizer is associated with an Aura RootWindow (ui/aura/root_window.h and ui/aura/root_window_host_linux.cc) and the recognizer instance is only invoked for touch events that "belong" to the respective root window. That is, we dispatch hit-testing and window identification tasks to Chromium in general and Aura in particular. Whenever the grail instance recognizes a gesture, we provide the surrounding framework with an instance of class aura::GestureEvent (see ui/aura/event.h). Please note that we modified the class to support pinch-gesture specific parameters, i.e., providing the current scale factor in x and y direction.
Please find a video demonstrating pixel perfect scrolling within Chromium Aura here and
. The screen cast has been recorded on the following setup:
- Precise Alpha
- frame and grail trunk versions
- Apple magic trackpad
And here is an overview of the architecture:
Summary & Open Issues
The patch accompanying this document introduces gesture recognition functionality to Chromium Aura based on frame and grail. To this end, we introduce a frame instance relying on its default X11 backend to the class ui::TouchFactory and provide an implementation of the interface aura::GestureRecognizer (see ui/aura/gestures/gesture_recognizer.h) in terms of grail (see ui/aura/gestures/gesture_recognizer_grail.h and .cc).
Abstracting Touch & Gesture Handling in Chromium
In the future, we might want to abstract the multi-touch event processing even more and move the frame instance away from class ui::TouchFactory to our implementation of interface aura::GestureRecognizer. To this end, we would need to provide a Chromium-specific backend to frame and alter the class aura::TouchEvent to provide all relevant information to frame. Moreover, we would need to introduce an event type to Chromium that models the addition and removal of multi-touch devices. We started with these additions recently and they are not finished yet. Despite that, we provide our current state here for the sake of reference and discussion. We started over by abstracting a touch device in the class ui::MultiTouchDevice (defined in ui/base/touch/multi_touch_device.h):
1 #ifndef UI_BASE_TOUCH_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_H
2 #define UI_BASE_TOUCH_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_H
3
4 #include "ui/base/touch/axis.h"
5
6 #include <iostream>
7 #include <map>
8 #include <string>
9 #include <vector>
10
11 namespace ui {
12
13 class MultiTouchDevice {
14 public:
15
16 typedef std::map<Axis::Type,Axis> Axes;
17
18 enum Type {
19 DIRECT_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE,
20 DEPENDENT_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE,
21 INDEPENDENT_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE,
22 SEMI_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE,
23 UNKNOWN_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE
24 };
25
26 MultiTouchDevice()
27 : id_(-1),
28 name_("Invalid touch device"),
29 type_(UNKNOWN_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE),
30 max_num_touches_(0),
31 window_resolution_x_(0.f),
32 window_resolution_y_(0.f) {
33 }
34
35 int id() const { return id_; }
36 void set_id(int id) { id_ = id; }
37
38 const std::string & name() const { return name_; }
39 void set_name(const std::string& name) { name_ = name; }
40
41 Type type() const { return type_; }
42 void set_type(Type type) { type_ = type; }
43
44 uint32_t max_num_touches() const { return max_num_touches_; }
45 void set_max_num_touches(uint32_t num) { max_num_touches_ = num; }
46
47 uint32_t num_axes() const { return axes_.size(); }
48
49 const Axes & axes() const { return axes_; }
50 void set_axes(const Axes & axes) { axes_ = axes; }
51
52 float window_resolution_x() const { return window_resolution_x_; }
53 void set_window_resolution_x(float res) { window_resolution_x_ = res; }
54
55 float window_resolution_y() const { return window_resolution_y_; }
56 void set_window_resolution_y(float res) { window_resolution_y_ = res; }
57
58 private:
59 int id_;
60 std::string name_;
61 Type type_;
62 uint32_t max_num_touches_;
63 Axes axes_;
64 float window_resolution_x_;
65 float window_resolution_y_;
66
67 // DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(MultiTouchDevice);
68 };
69
70 std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream & out, const MultiTouchDevice& device);
71
72 }
73
74 #endif // UI_BASE_TOUCH_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_H
75
That is, every device is uniquely identified by an id, it provides a human-readable name, information on its type (direct vs. dependent touch devices) and a look-up table of its supported axes. An axis is abstracted by class ui::!Axis (defined in ui/base/touch/axis.h):
1 #ifndef UI_BASE_TOUCH_AXIS_H
2 #define UI_BASE_TOUCH_AXIS_H
3
4 #include "base/property_bag.h"
5
6 #include <iostream>
7 #include <limits>
8 #include <string>
9
10 namespace ui {
11
12 class Axis {
13 public:
14
15 enum Type {
16 AXIS_TYPE_X = 0, /**< X coordinate */
17 AXIS_TYPE_Y, /**< Y coordinate */
18 AXIS_TYPE_TOUCH_MAJOR, /**< Width along major axis of contact area of touch */
19 AXIS_TYPE_TOUCH_MINOR, /**< Width along minor axis of contact area of touch */
20 AXIS_TYPE_WIDTH_MAJOR, /**< Width along major axis of touch tool */
21 AXIS_TYPE_WIDTH_MINOR, /**< Width along minor axis of touch tool */
22 AXIS_TYPE_ORIENTATION, /**< Orientation of major axis of contact ellipse */
23 AXIS_TYPE_TOOL, /**< Tool type */
24 AXIS_TYPE_BLOB_ID, /**< Blob ID of group of touches */
25 AXIS_TYPE_TRACKING_ID, /**< Tracking ID */
26 AXIS_TYPE_PRESSURE, /**< Pressure */
27 AXIS_TYPE_HOVER_DISTANCE, /**< Hover distance */
28 AXIS_TYPE_UNKNOWN,
29 AXIS_TYPE_LAST
30 };
31
32 Axis()
33 : id_(-1),
34 type_(AXIS_TYPE_UNKNOWN),
35 name_("Unknown axis"),
36 min_(-std::numeric_limits<float>::max()),
37 max_(std::numeric_limits<float>::max()),
38 resolution_(0.f),
39 value_(0.f),
40 payload_(NULL) {
41 }
42
43 ~Axis() {
44 delete(payload_);
45 }
46
47 int id() const { return id_; }
48 void set_id(int id) { id_ = id; }
49
50 Type type() const { return type_; }
51 void set_type(Type type) { type_ = type; }
52
53 const std::string & name() const { return name_; }
54 void set_name(const std::string& name) { name_ = name; }
55
56 float min() const { return min_; }
57 void set_min(float min) { min_ = min; }
58
59 float max() const { return max_; }
60 void set_max(float max) { max_ = max; }
61
62 float resolution() const { return resolution_; }
63 void set_resolution(float res) { resolution_ = res; }
64
65 float value() const { return value_; }
66 void set_value(float value) { value_ = value; }
67
68 base::PropertyBag * payload() {
69 if(payload_ == NULL)
70 payload_ = new base::PropertyBag();
71
72 return payload_;
73 }
74
75 private:
76 int id_;
77 Type type_;
78 std::string name_;
79 float min_;
80 float max_;
81 float resolution_;
82 float value_;
83 base::PropertyBag* payload_;
84 };
85
86 std::ostream & operator<<(std::ostream& out, const Axis& axis);
87
88 }
89
90 #endif // UI_BASE_TOUCH_AXIS_H
91
Platform/toolkit-specific initialization tasks are implemented in terms of free functions. For X11, an example can be found in ui/base/touch/multi_touch_device_x11.h and .cc:
1 #ifndef UI_BASE_TOUCH_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_X11_H
2 #define UI_BASE_TOUCH_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_X11_H
3
4 #include <X11/extensions/XInput.h>
5 #include <X11/extensions/XInput2.h>
6
7 namespace ui {
8
9 class MultiTouchDevice;
10
11 bool xi_device_info_to_mt_device(XIDeviceInfo * info,
12 MultiTouchDevice & out);
13
14 }
15
16 #endif // UI_BASE_TOUCH_MULTI_TOUCH_DEVICE_X11_H
17
1 #include "ui/base/touch/multi_touch_device_x11.h"
2
3 #include "ui/base/touch/multi_touch_device.h"
4
5 #include "ui/base/x/x11_util.h"
6
7 #include <xorg/xserver-properties.h>
8
9 #include <X11/extensions/XInput.h>
10 #include <X11/extensions/XInput2.h>
11 #include <X11/extensions/XIproto.h>
12
13 namespace {
14
15 const char * AxisNameForType(ui::Axis::Type type) {
16
17 // Defines are taken from xorg/xserver-properties.h
18 static const char* names[ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_LAST+1] = {
19 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_POSITION_X,
20 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_POSITION_Y,
21 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR,
22 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TOUCH_MINOR,
23 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_WIDTH_MAJOR,
24 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_WIDTH_MINOR,
25 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_ORIENTATION,
26 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TOOL_TYPE,
27 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_BLOB_ID,
28 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID,
29 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_PRESSURE,
30 AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MISC,
31 "Unknown axis type",
32 "ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_LAST"
33 };
34
35 return names[type];
36 }
37
38 ui::Axis::Type AxisTypeForLabel(Display* display, Atom label) {
39 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TOUCH_MAJOR,
40 True))
41 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_TOUCH_MAJOR;
42 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TOUCH_MINOR,
43 True))
44 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_TOUCH_MINOR;
45 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_WIDTH_MAJOR,
46 True))
47 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_WIDTH_MAJOR;
48 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_WIDTH_MINOR,
49 True))
50 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_WIDTH_MINOR;
51 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_ORIENTATION,
52 True))
53 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_ORIENTATION;
54 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TOOL_TYPE,
55 True))
56 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_TOOL;
57 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_BLOB_ID,
58 True))
59 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_BLOB_ID;
60 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID,
61 True))
62 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_TRACKING_ID;
63 if (label == XInternAtom(display, AXIS_LABEL_PROP_ABS_MT_PRESSURE,
64 True))
65 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_PRESSURE;
66
67 return ui::Axis::AXIS_TYPE_UNKNOWN;
68 }
69
70 } // namespace
71
72 namespace ui {
73 bool xi_device_info_to_mt_device(XIDeviceInfo * info,
74 MultiTouchDevice & out) {
75
76 if(info == NULL)
77 return false;
78
79 out.set_id(info->deviceid);
80 out.set_name(info->name);
81 MultiTouchDevice::Axes axes;
82
83 for (int i = 0; i < info->num_classes; ++i) {
84 switch (info->classes[i]->type) {
85 case XITouchClass: {
86 XITouchClassInfo* touch_info =
87 reinterpret_cast<XITouchClassInfo*>(info->classes[i]);
88
89 switch(touch_info->mode) {
90 case XIDirectTouch:
91 out.set_type(MultiTouchDevice::DIRECT_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE);
92 break;
93 case XIDependentTouch:
94 out.set_type(MultiTouchDevice::DEPENDENT_TOUCH_DEVICE_TYPE);
95 break;
96 }
97
98 out.set_max_num_touches(touch_info->num_touches);
99 break;
100 }
101
102 case XIValuatorClass: {
103 XIValuatorClassInfo* valuator_info =
104 reinterpret_cast<XIValuatorClassInfo*>(info->classes[i]);
105
106 Axis::Type type;
107
108 /* X and Y axes are always 0 and 1 in X11. Due to historical reasons,
109 * the labels of these axes may not be consistent across input modules.
110 * Hard code them here instead. */
111 if (valuator_info->number == 0)
112 type = Axis::AXIS_TYPE_X;
113 else if (valuator_info->number == 1)
114 type = Axis::AXIS_TYPE_Y;
115 else {
116 type = AxisTypeForLabel(ui::GetXDisplay(), valuator_info->label);
117 }
118
119 if(type==Axis::AXIS_TYPE_UNKNOWN)
120 continue;
121
122 Axis axis;
123 axis.set_name(AxisNameForType(type));
124 axis.set_type(type);
125 axis.set_min(valuator_info->min);
126 axis.set_max(valuator_info->max);
127 axis.set_resolution(valuator_info->resolution);
128
129 axes[type] = axis;
130
131 break;
132 }
133
134 default:
135 break;
136 }
137 }
138
139 out.set_axes(axes);
140
141 out.set_window_resolution_x(0.f);
142 out.set_window_resolution_y(0.f);
143
144 return true;
145 }
146
147 }
Given an X11-specific description of a multi-touch device, an instance of the Chromium-specific abstraction ui::MultiTouchDevice is initialized with device-specific information. Dispatching platform/toolkit-specific events is carried out by the singleton ui::TouchFactory. Reporting the results to the console, the following output is obtained when starting up Chromium Aura on our test setup (see before):
MultiTouchDevice: Virtual core pointer
id: 2
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position X
type: 0
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 1
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position Y
type: 1
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 1
value: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Virtual core keyboard
id: 3
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Virtual core XTEST pointer
id: 4
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position X
type: 0
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 0
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position Y
type: 1
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 0
value: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Virtual core XTEST keyboard
id: 5
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Power Button
id: 6
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Video Bus
id: 7
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Sleep Button
id: 8
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Integrated Camera
id: 9
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: AT Translated Set 2 keyboard
id: 10
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: SynPS/2 Synaptics TouchPad
id: 11
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position X
type: 0
min: 1472
max: 5472
resolution: 73000
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position Y
type: 1
min: 1408
max: 4448
resolution: 75000
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Pressure
type: 10
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 0
value: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: ThinkPad Extra Buttons
id: 12
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: TPPS/2 IBM TrackPoint
id: 13
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position X
type: 0
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 1
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position Y
type: 1
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 1
value: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: ThinkPad Bluetooth Laser Mouse
id: 14
type: 4
max_num_touches: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position X
type: 0
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 1
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position Y
type: 1
min: -1
max: -1
resolution: 1
value: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0
MultiTouchDevice: Apple Wireless Trackpad
id: 15
type: 1
max_num_touches: 5
Axis: Abs MT Position X
type: 0
min: -2909
max: 3167
resolution: 46000
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Position Y
type: 1
min: -2456
max: 2565
resolution: 45000
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Touch Major
type: 2
min: 0
max: 255
resolution: 0
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Touch Minor
type: 3
min: 0
max: 255
resolution: 0
value: 0
Axis: Abs MT Orientation
type: 6
min: -31
max: 32
resolution: 0
value: 0
window_resolution_x: 0
window_resolution_y: 0Nevertheless, by abstracting touch-event handling on top of chromium, we do not need to take care of platform specific issues in frame but dispatch the platform-specific tasks to Chromium.
Please see the Chromium gesture blueprint for work item details.
Multitouch/CurrentWork/ChromiumTouch (last edited 2012-06-14 19:53:13 by c-67-170-185-42)